Irofulveno
compuesto químico
El irofulveno o 6-hidroximetilacilfulveno (también conocido como HMAF de MGI-114) es un agente antitumoral experimental.[2][3] Pertenece a la familia de fármacos denominados agentes alquilantes.
| Irofulveno | ||
|---|---|---|
 | ||
| Nombre IUPAC | ||
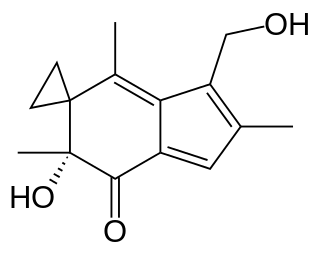
| (6′R)-6′-Hidroxi-3′-(hidroximetil)-2′,4′,6′-trimetilespiro[ciclopropano-1,5′-inden]-7′(6′H)-ona | ||
| General | ||
| Fórmula estructural |
 | |
| Fórmula molecular | C15H18O3 | |
| Identificadores | ||
| Número CAS | 158440-71-2[1] | |
| ChEBI | 135002 | |
| ChEMBL | 118218 | |
| ChemSpider | 130640 | |
| DrugBank | DB05786 | |
| PubChem | 148189 | |
| UNII | 6B799IH05A | |
| KEGG | D04614 | |
|
O=C1C/3=C/C(=C(C\3=C(/C2([C@]1(O)C)CC2)C)CO)C
| ||
| Propiedades físicas | ||
| Masa molar | 246,302 g/mol | |
| Valores en el SI y en condiciones estándar (25 ℃ y 1 atm), salvo que se indique lo contrario. | ||
Inhibe la replicación del ADN en cultivos celulares.[4]
El irofulveno es un análogo de la iludina S, una toxina sesquiterpénica que se encuentra en el hongo Jack 'o' jantern (Omphalotus illudens). El compuesto fue sintetizado originalmente por el Dr Trevor McMorris y el Dr. Michael J Kelner descubrió que tiene propiedades anticancerígenas en ratones.[5]
Síntesis
editarSe informó una síntesis de irofulven.[6]
Referencias
editar- ↑ Número CAS
- ↑ Escargueil, A. E.; Poindessous, V.; Soares, D. G.; Sarasin, A.; Cook, P. R.; Larsen, A. K. (April 2008). «Influence of Irofulven, a Transcription-Coupled Repair-Specific Antitumor Agent, on RNA Polymerase Activity, Stability and Dynamics in Living Mammalian Cells». Journal of Cell Science 121 (Pt 8): 1275-1283. PMID 18388315. doi:10.1242/jcs.023259.
- ↑ Kelner, M. J.; McMorris, T. C.; Estes, L.; Wang, W.; Samson, K. M.; Taetle, R. (1996). «Efficacy of HMAF (MGI-114) in the MV522 Metastatic Lung Carcinoma Xenograft Model Nonresponsive to Traditional Anticancer Agents». Investigational New Drugs 14 (2): 161-167. PMID 8913837. S2CID 8439510. doi:10.1007/BF00210787.
- ↑ Wang, Y.; Wiltshire, T.; Senft, J.; Reed, E.; Wang, W. (February 2007). «Irofulven Induces Replication-Dependent CHK2 Activation Related to p53 Status». Biochemical Pharmacology 73 (4): 469-480. PMC 1800887. PMID 17118344. doi:10.1016/j.bcp.2006.10.023.
- ↑ MacDonald, J. R.; Muscoplat, C. C.; Dexter, D. L.; Mangold, G. L.; Chen, S. F.; Kelner, M. J.; McMorris, T. C.; Von Hoff, D. D. (1997). «Preclinical Antitumor Activity of 6-hydroxymethylacylfulvene, a Semisynthetic Derivative of the Mushroom Toxin Illudin S». Cancer Research 57 (2): 279-283. PMID 9000568.
- ↑ McMorris, T. C.; Staake, M. D.; Kelner, M. J. (2004). «Synthesis and Biological Activity of Enantiomers of Antitumor Irofulven». The Journal of Organic Chemistry 69 (3): 619-23. PMID 14750783. doi:10.1021/jo035084j.